Physiotherapy is used to treat conditions relating to your bones, joints, ligaments and tendons.
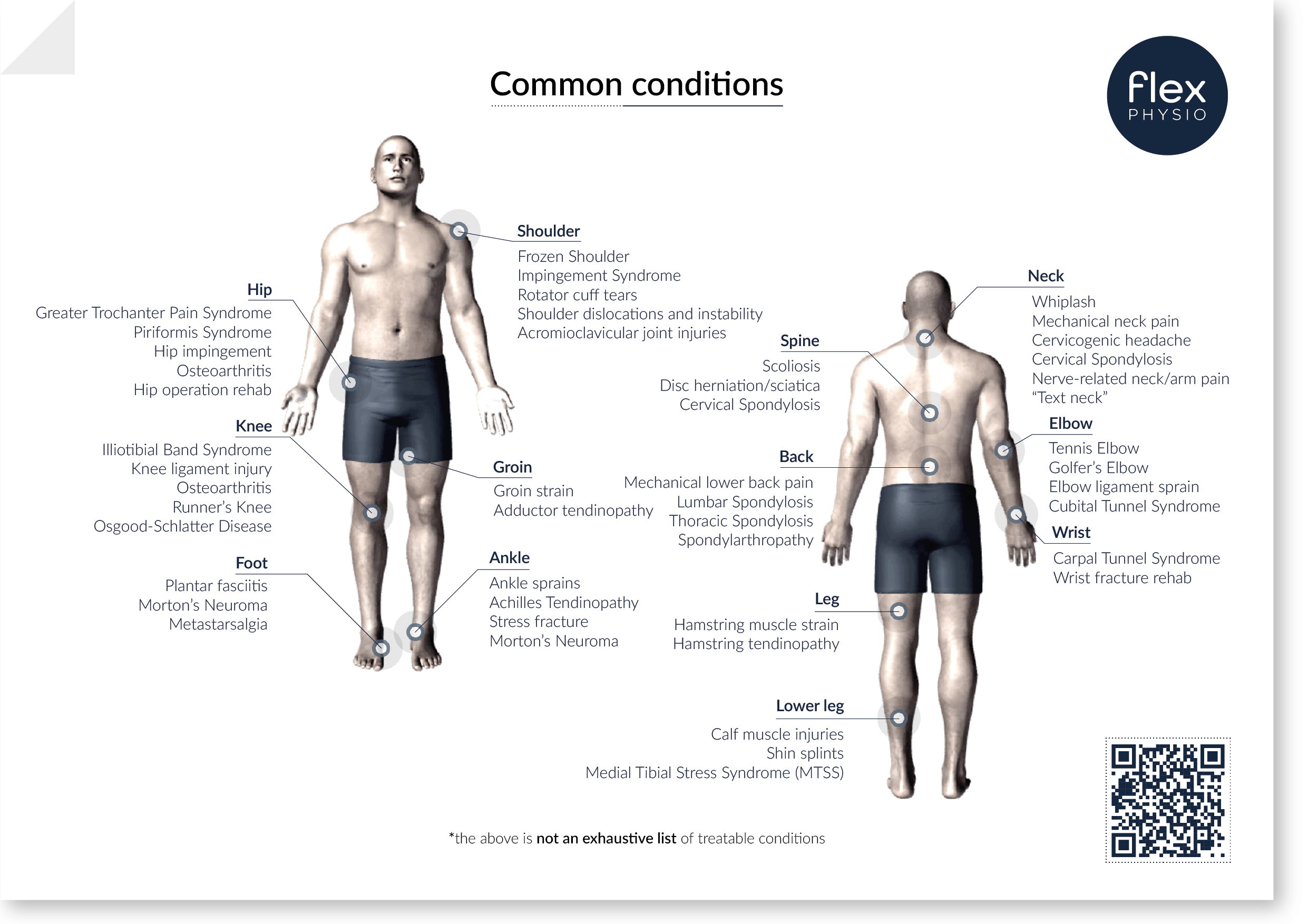
Physiotherapy is concerned with the assessment, diagnosis, and treatment of a wide range of “musculoskeletal” conditions.
What does “musculoskeletal” mean?
Our bones, joints, ligaments and tendons make up our “musculoskeletal” system. Problems or injuries that affect these muscles and skeletal structures – such as pain, stiffness, strains, sprains, fractures, or diseases like arthritis – can be treated by physotherapists. Physiotherapists specialize in assessing and treating these conditions, employing various techniques and exercises to help improve movement, reduce pain, and enhance overall function.
Below we’ll explore several common conditions affecting different body parts and highlight the physiotherapy treatments used to address them.
“Our bones, joints, ligaments and tendons make up our ‘musculoskeletal’ system.”
Leg:
- Tendinopathy: Tendinopathy refers to the inflammation or degeneration of a tendon, which connects muscles to bones. Physiotherapists can employ a combination of exercises, manual therapy, and modalities like ultrasound or laser therapy to stimulate healing, reduce pain, and improve the strength and flexibility of the affected tendon.
- Calf Muscle Injuries: Calf muscle injuries, such as strains or tears, can result from sudden movements or overuse. Physiotherapy for calf injuries may involve stretching and strengthening exercises, massage, and gradual progression of activity to promote healing and prevent re-injury.
- Shin Splints, Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome (MTSS): Shin splints and MTSS are conditions characterized by pain along the shinbone (tibia). Physiotherapists employ various techniques like stretching, strengthening exercises, gait analysis, and footwear recommendations to alleviate pain, address contributing factors (such as muscle imbalances), and facilitate a safe return to activity.
Back:
- Lumbar or Thoracic Spondylosis: Lumbar or thoracic spondylosis refers to degenerative changes in the spine, such as the formation of bone spurs or disc degeneration. Physiotherapy treatments may involve exercises to improve posture, strengthen core muscles, and enhance spinal flexibility. Manual therapy techniques, including mobilization or manipulation, can also be used to manage pain and improve joint mobility.
- Spondylarthropathy: Spondylarthropathy encompasses a group of inflammatory conditions affecting the spine, such as ankylosing spondylitis. Physiotherapy aims to reduce pain, maintain joint mobility, and improve posture through exercises, postural education, and breathing techniques. Additionally, hydrotherapy and heat/cold therapy may be employed to manage symptoms.
- Mechanical Lower Back Pain: Mechanical lower back pain refers to pain originating from the structures of the spine, including muscles, ligaments, or discs. Physiotherapy treatments often involve a combination of manual therapy techniques, therapeutic exercises, and education on ergonomics and body mechanics. The goal is to reduce pain, improve spinal stability, and enhance overall function.
Knee:
- Runner’s Knee: Runner’s Knee, or patellofemoral pain syndrome, involves pain around or behind the kneecap. Physiotherapy treatments for Runner’s Knee focus on strengthening the hip and thigh muscles, correcting biomechanical imbalances, and providing guidance on proper footwear and training techniques.
- Osteoarthritis: Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint condition that commonly affects the knee. Physiotherapists employ exercises to improve joint mobility, strengthen surrounding muscles, and reduce pain. They may also use modalities like heat, cold, or electrical stimulation to manage symptoms.
- Iliotibial Band Syndrome: Iliotibial Band Syndrome is characterized by pain on the outer side of the knee. Physiotherapy treatment typically involves stretching and strengthening exercises, foam rolling, and addressing contributing factors such as hip weakness or improper running mechanics.
Hip:
- Hip Impingement: Hip impingement, or femoroacetabular impingement (FAI), occurs when there is abnormal contact between the hip joint’s bones, leading to pain and limited range of motion. Physiotherapy interventions often involve targeted exercises to improve hip mobility, strengthen surrounding muscles, and optimize movement patterns.
- Greater Trochanter Pain Syndrome: Greater Trochanter Pain Syndrome refers to pain on the outside of the hip. Physiotherapists may use manual therapy techniques, such as soft tissue mobilization, along with exercise programs aimed at improving hip stability, flexibility, and muscle balance.
- Hip Operation Rehabilitation: Physiotherapy plays a crucial role in the rehabilitation following hip operations, such as hip replacements or arthroscopic procedures. Treatment focuses on restoring range of motion, strength, and function through specific exercises, gait training, and gradual progression of activities.
Shoulder:
- Frozen Shoulder: Frozen Shoulder, or adhesive capsulitis, involves pain and stiffness in the shoulder joint. Physiotherapy interventions include gentle stretching exercises, joint mobilization techniques, and modalities like heat or cold therapy to alleviate pain and restore shoulder mobility.
- Rotator Cuff Tears: Rotator cuff tears are injuries to the tendons surrounding the shoulder joint. Physiotherapy treatment often includes exercises to strengthen the rotator cuff muscles, improve shoulder stability, and enhance shoulder mechanics. Manual therapy techniques and modalities may be employed to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Shoulder Dislocations and Instability: Physiotherapy for shoulder dislocations and instability aims to strengthen the shoulder muscles, improve joint stability, and enhance proprioception (awareness of joint position). This is achieved through exercises, functional training, and targeted rehabilitation protocols.
Neck:
- Whiplash: Whiplash is an injury commonly resulting from a sudden jolt to the neck, such as during a car accident. Physiotherapy treatments may include gentle range of motion exercises, manual therapy techniques, and modalities like heat or electrical stimulation to alleviate pain, restore neck mobility, and improve muscle strength.
- Mechanical Neck Pain: Mechanical neck pain refers to pain arising from the structures in the neck, such as muscles, joints, or ligaments. Physiotherapy interventions often involve a combination of manual therapy, postural correction exercises, and strengthening exercises to reduce pain, improve mobility, and enhance posture.
- “Text Neck”: “Text Neck” is a term used to describe neck pain and stiffness caused by prolonged and improper use of mobile devices. Physiotherapy for “Text Neck” focuses on postural correction, strengthening exercises for the neck and upper back muscles, and providing education on ergonomic practices.
Spine:
- Scoliosis: Scoliosis is a condition characterized by abnormal sideways curvature of the spine. Physiotherapy interventions aim to improve postural alignment, enhance core strength, and optimize spinal mobility through exercises, bracing (in certain cases), and postural education.
- Disc Herniation/Sciatica: Disc herniation occurs when the cushioning discs between the vertebrae bulge or rupture, potentially compressing spinal nerves and causing sciatica. Physiotherapy for disc herniation and sciatica often involves a combination of manual therapy, exercises to improve spinal stability and flexibility, and pain management strategies.
Elbow:
- Tennis Elbow: Tennis Elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, is characterized by pain on the outer side of the elbow. Physiotherapy treatments typically include exercises to improve forearm muscle strength and flexibility, manual therapy techniques, and modifications to activity or technique to promote healing and prevent re-injury.
- Golfer’s Elbow: Golfer’s Elbow, or medial epicondylitis, involves pain on the inner side of the elbow. Physiotherapy interventions for Golfer’s Elbow often include stretching and strengthening exercises, manual therapy techniques, and activity modifications to reduce pain and promote healing.
- Elbow Ligament Sprain: Elbow ligament sprains, such as a sprained ulnar collateral ligament (UCL), may require physiotherapy interventions that focus on strengthening the surrounding muscles, improving joint stability, and gradually restoring functional activities through exercises and progressive rehabilitation protocols.
Wrist:
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Carpal Tunnel Syndrome involves compression of the median nerve in the wrist, leading to symptoms like pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand and fingers. Physiotherapy treatments may include exercises to improve wrist mobility and strength, ergonomic modifications, and splinting to alleviate symptoms and improve function.
- Wrist Fracture Rehabilitation: Following a wrist fracture, physiotherapy plays a vital role in restoring range of motion, strength, and functional abilities. Treatment may involve exercises for wrist mobility and strengthening, manual therapy techniques, and gradual reintegration into daily activities.
Groin:
- Groin Strain: A groin strain refers to an injury or tear in the muscles of the inner thigh or groin area. Physiotherapy treatments often include stretching, strengthening exercises, manual therapy techniques, and modalities like heat or cold therapy to promote healing, reduce pain, and restore muscle function.
- Adductor Tendinopathy: Adductor tendinopathy involves pain and inflammation of the tendons in the groin area. Physiotherapy interventions may include specific exercises to strengthen the adductor muscles, manual therapy techniques, and activity modifications to manage symptoms and facilitate tendon healing.
Ankle:
- Ankle Sprains: Ankle sprains occur when the ligaments supporting the ankle joint are stretched or torn. Physiotherapy treatments for ankle sprains typically involve exercises to improve balance, strength, and range of motion, along with manual therapy techniques and functional training to facilitate a safe return to activity.
- Achilles Tendinopathy: Achilles tendinopathy is characterized by pain and degeneration of the Achilles tendon. Physiotherapy interventions often include eccentric strengthening exercises, stretching, modalities for pain management, and biomechanical assessments to address contributing factors and promote tendon healing.
- Morton’s Neuroma: Morton’s Neuroma involves the thickening of tissue around a nerve in the ball of the foot, leading to pain and numbness. Physiotherapy treatments may include foot and ankle mobilization, orthotic recommendations, and exercises to improve foot mechanics and alleviate symptoms.
Foot:
- Plantar Fasciitis: Plantar Fasciitis is the inflammation of the plantar fascia, causing heel pain. Physiotherapy interventions commonly include stretching exercises, foot mobilization, orthotic recommendations, and modalities like ultrasound or shockwave therapy to reduce pain, promote healing, and improve foot mechanics.
- Metatarsalgia: Metatarsalgia refers to pain and inflammation in the ball of the foot. Physiotherapy treatments for metatarsalgia often involve foot and ankle strengthening exercises, activity modifications, and orthotic recommendations to relieve pressure, reduce pain, and restore function.